Tool development
We have developed techniques to very efficiently knock-in epitopes into endogenous loci using oligonucleotides and CRISPR/Cas9. By selecting for repair of a temperature-sensitive, conditional lethal mutation, we were able to significantly enrich for knock-ins at a second, unlinked locus (Ward, 2015). The stringency of this co-selection allowed optimization of numerous oligo-editing parameters (i.e., homology length, DSB position, oligo polarity). We have avidly been working to optimize the auxin-inducible degron system in C. elegans (Zhang et al., 2015, Martinez et al., 2020). We have recently generated a set of single-copy, tissue-specific (germline, intestine, neuron, muscle, hypodermis, seam cell, anchor cell) and pan-somatic TIR1-expressing strains carrying an equimolar co-expressed blue fluorescent reporter to enable use of both red and green channels in experiments (Ashley et al., 2021). We have also constructed a set of plasmids to generate fluorescent protein::AID fusions through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editingd. This battery of new TIR1-expressing strains and modular, efficient cloning vectors serves as a platform for facile assembly of CRISPR/Cas9 repair templates for conditional protein depletion. Together, these approaches allow C. elegans researchers to make edits at will in the genome, and rapidly deplete degron-tagged proteins with temporal and cell-specific precision. We have also developed methods to use mammalian steroid receptor ligand-binding domain (LBD) fusions to conditionally activate C. elegans proteins (Monsalve et al., 2019). These experiments provided a powerful tool for temporal control of protein activity, and bolster existing tools used to modulate gene expression and protein activity in C. elegans.
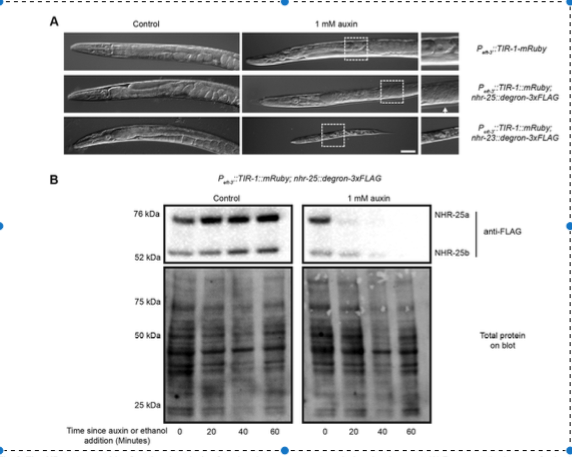
The AID system enables functional analysis of nuclear hormone receptors during development. From Zhang et al., 2015. (A) Representative images of animals from the timed egg lay on control or 1 mM auxin plates following 60 h at 25°C. In the absence of auxin, no defects were seen in any genotype; however, in the presence of auxin, worms expressing degron-tagged NHR-25 and pan-somatic TIR1 showed molting defects (arrow indicated unshed cuticle) and gonadal defects such as tumorous germ lines (note lack of eggs and abnormal germ line). Animals expressing degron-tagged NHR-23 and pan-somatic TIR1 uniformly arrested as L1 larvae. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Temporal analysis of inducible protein degradation. Worms of the indicated genotypes were grown for six hours at 25°C following dauer release before 0.25% ethanol (control) or 1 mM auxin were added and samples harvested every 20 min. Lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Stain-free (Bio-Rad) analysis of total protein on each blot is provided as a loading control. Two isoforms of NHR-25 (a and b) are detected, as previously described (Ward, 2015).